Project Overview
This project demonstrates how advanced computer vision can transform industrial quality control. I developed an AI-powered defect detection system that automatically identifies faulty wall plugs in manufacturing production lines—achieving performance comparable to commercial systems costing over $15,000, while operating at approximately 10% of that price on low-cost hardware like a Raspberry Pi.
The system represents a lightweight reconstruction of industrial-grade computer vision technology, designed to reduce waste, improve manufacturing consistency, and minimize manual inspection costs by catching defects early in the production process.
Problem Statement
Manual visual inspection in manufacturing is time-consuming, monotonous, and prone to human error. Even experienced inspectors can miss defects, especially during long shifts, leading to:
- Increased waste from defects caught late in production
- Higher costs from manual labor and rework
- Inconsistent quality due to human fatigue
- Slower throughput in production lines
The challenge was to build an automated system that could reliably identify defects across multiple wall plug types while remaining affordable and transparent enough for real-world industrial deployment.
Technical Approach
Dataset & Training
The system was trained on a carefully curated dataset of approximately 500 labeled images representing four distinct wall plug types:
- Frame fixing plugs
- Insulation anchors
- Ribbed wall plugs
- Toggle anchors
After establishing a human-level accuracy benchmark of 95%, I followed an iterative development process to progressively improve model performance.
Model Development
Phase 1: Baseline Neural Network
- Simple feedforward neural network architecture
- Achieved 84% accuracy
- Established baseline performance metrics
Phase 2: Custom Convolutional Network
- Designed custom CNN architecture optimized for wall plug features
- Improved accuracy to 90%
- Demonstrated value of spatial feature extraction
Phase 3: Advanced Techniques
- Applied data augmentation (rotation, scaling, brightness adjustment)
- Implemented transfer learning with pre-trained models:
- MobileNetV2: Optimized for mobile/edge deployment
- EfficientNetB0: Balanced accuracy and efficiency
- Final result: 100% accuracy on test set
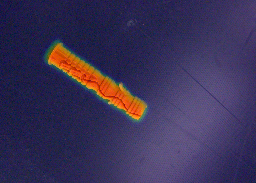
Explainable AI Integration
To ensure the system’s decisions could be verified and trusted in a production environment, I integrated Grad-CAM (Gradient-weighted Class Activation Mapping) visualizations. This technique highlights which regions of an image influenced the model’s predictions, allowing:
- Quality control operators to verify decisions
- Engineers to debug misclassifications
- Stakeholders to understand model reasoning
- Continuous improvement through insight into model behavior
User Interface
I developed a user-friendly desktop application with the following features:
Core Functionality:
- Single image classification: Upload and analyze individual images
- Batch processing: Classify multiple images simultaneously
- Real-time results: Instant defect detection with confidence scores
Explainability Features:
- Grad-CAM heatmaps: Visual explanation of model decisions
- Confidence metrics: Transparency in prediction certainty
- Decision logs: Audit trail for quality assurance
Usability Design:
- Intuitive layout confirmed through user testing
- Clear visual feedback and guidance
- Streamlined workflow for production environments
Results & Impact
Performance Metrics
- Accuracy: 100% on test dataset
- Speed: Real-time inference on low-cost hardware
- Reliability: Exceeded human-level benchmark (95%)
- Cost: ~10% of commercial systems ($1,500 vs $15,000+)
Usability Validation
Conducted usability studies with potential end-users, receiving positive feedback on:
- Interface clarity and ease of use
- Speed and efficiency of workflow
- Trustworthiness of XAI explanations
Implemented improvements based on user feedback to enhance layout and guidance.
Business Value
- Reduced waste: Early defect detection prevents downstream rework
- Lower costs: Affordable alternative to expensive commercial systems
- Improved consistency: Eliminates human fatigue factor
- Scalability: Can be deployed across multiple production lines
- Edge deployment: Runs efficiently on Raspberry Pi hardware
Key Learnings
Transfer Learning is Powerful: Pre-trained models like MobileNetV2 and EfficientNetB0 provided an excellent starting point, dramatically reducing training time and improving accuracy.
Explainability Matters: In industrial settings, black-box predictions aren’t enough. Grad-CAM visualizations proved essential for building trust and enabling operators to verify decisions.
User-Centered Design: Early user testing revealed usability issues that weren’t obvious during development. Iterative feedback improved the interface significantly.
Edge Deployment Feasibility: Modern neural networks can run efficiently on low-cost hardware, making advanced AI accessible to small and medium manufacturers.
Future Enhancements
- Real-time video processing: Continuous monitoring on production lines
- Multi-defect detection: Simultaneous identification of multiple defect types
- Anomaly detection: Identifying unknown defect patterns
- Cloud integration: Centralized monitoring across multiple facilities
- Automated retraining: Continuous learning from production data
Technologies Used
Machine Learning Framework: TensorFlow/Keras
Pre-trained Models: MobileNetV2, EfficientNetB0
Explainable AI: Grad-CAM
Computer Vision: OpenCV, PIL
Hardware: Raspberry Pi 4, Standard webcam/industrial camera
Interface: Python (Streamlit)
Data Processing: NumPy, Pandas, Matplotlib
Conclusion
This project demonstrates that sophisticated quality control systems don’t require enterprise-level budgets. By leveraging transfer learning, explainable AI, and efficient neural network architectures, manufacturers can deploy affordable, reliable defect detection systems that rival commercial solutions at a fraction of the cost.
The system proves that advanced AI technology is accessible and practical for small to medium-sized manufacturers, opening new possibilities for automated quality assurance across the industry.